Estimating the relative biological effectiveness of neutron radiation for inducing clustered DNA damage via Monte Carlo simulation of direct and indirect action
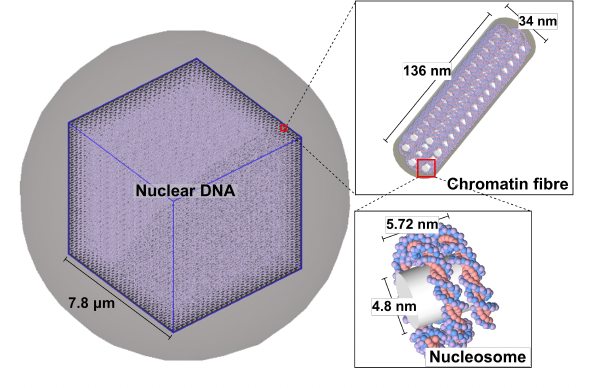 Image credit: James Manalad
Image credit: James ManaladAbstract
Purpose: Exposure to ionizing radiation can induce stochastic biological effects in the human body. For neutrons, the risk of these biological effects is energy dependent and previous Monte Carlo studies have linked this dependence with the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of neutrons to induce difficult-to-repair clusters of DNA damage (CDDs). However, these studies have only modeled direct radiation action, excluding the potentially influential effects of indirect action. In this project, we investigated the effects of indirect action on CDDs and estimated the CDD-induction RBE of neutrons due to the combined effects of direct and indirect action. Methods: An existing Monte Carlo track-structure pipeline of our group was updated to include indirect action. Following this update, we simulated the irradiation of our custom nuclear DNA model (built using TOPAS-nBio) by monoenergetic neutrons and reference X-rays. The resulting CDDs were analyzed and compared to determine energy-dependent neutron RBE. Results: With indirect action included, we found a significant increase in CDD yields, cluster length, and lesion count per cluster. Our estimated energy-dependent neutron RBE followed the same trend as previous findings, but is lower in magnitude because the relative damage impact of indirect action was greater for X-rays than for neutrons. Conclusions: We have demonstrated the significant influence of indirect action in radiation-induced CDDs. Our findings suggest that the energy-dependent risk of neutron-induced stochastic effects is related to, but not completely explained by, the induction of CDDs. Thus, the investigation of factors such as DNA damage repair and non-targeted radiation effects is warranted.